Worksheet about speed velocity and acceleration – Unveiling the intricacies of motion, the worksheet on speed, velocity, and acceleration embarks on an enlightening journey. This meticulously crafted resource unravels the fundamental concepts that govern the dynamics of objects, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential physical quantities.
Through a harmonious blend of theoretical explanations, illustrative examples, and practical applications, this worksheet empowers learners to grasp the nuances of speed, velocity, and acceleration, equipping them with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of motion in the real world.
Worksheet about Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration

Speed, velocity, and acceleration are three fundamental concepts in physics that describe the motion of objects. This worksheet provides an introduction to these concepts, including their definitions, units of measurement, and examples.
Explain the concept of speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Speedis the rate at which an object changes its position over time. It is a scalar quantity, meaning that it has only magnitude and no direction. The SI unit of speed is meters per second (m/s).
Velocityis the rate at which an object changes its position over time, including both magnitude and direction. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s).
Accelerationis the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²).
Provide examples to illustrate the difference between speed, velocity, and acceleration., Worksheet about speed velocity and acceleration
- A car traveling at a constant speed of 60 mph has a speed of 60 mph but no acceleration.
- A car traveling at a constant velocity of 60 mph north has a velocity of 60 mph north and no acceleration.
- A car traveling at a constant acceleration of 2 m/s² has a velocity that is increasing by 2 m/s every second.
Discuss the units of measurement for speed, velocity, and acceleration.
The SI units of speed, velocity, and acceleration are:
- Speed: meters per second (m/s)
- Velocity: meters per second (m/s)
- Acceleration: meters per second squared (m/s²)
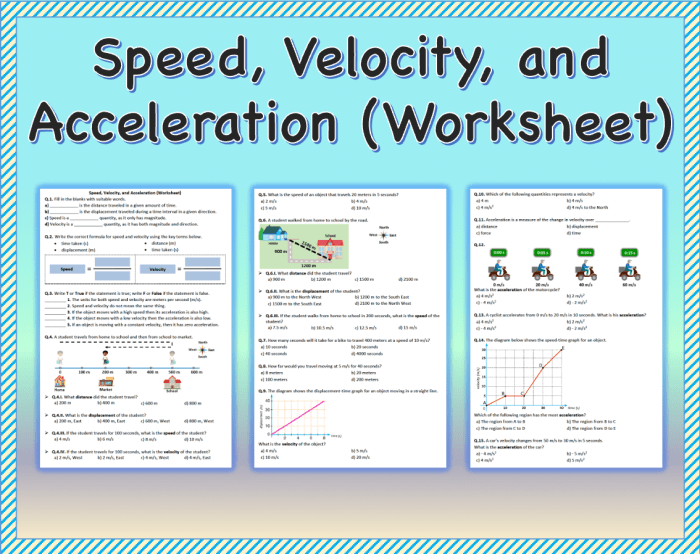
Solving Problems Related to Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Worksheet About Speed Velocity And Acceleration
Design a set of practice problems that involve calculating speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Problem 1:A car travels 100 km in 2 hours. What is its average speed?
Problem 2:A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10 m/s. What is its velocity after 1 second?
Problem 3:A car accelerates from rest to a velocity of 60 mph in 10 seconds. What is its average acceleration?
Provide step-by-step s on how to solve these problems.
Problem 1:
- Convert the distance to meters: 100 km = 100,000 m
- Convert the time to seconds: 2 hours = 7,200 seconds
- Calculate the average speed: speed = distance / time = 100,000 m / 7,200 s = 13.89 m/s
Problem 2:
- The acceleration due to gravity is
9.8 m/s².
- Use the equation: velocity = initial velocity + acceleration × time
- Calculate the velocity after 1 second: velocity = 10 m/s + (-9.8 m/s²) × 1 s = 0.2 m/s
Problem 3:
- Convert the velocity to m/s: 60 mph = 26.82 m/s
- Use the equation: acceleration = (final velocity
initial velocity) / time
- Calculate the average acceleration: acceleration = (26.82 m/s
0 m/s) / 10 s = 2.68 m/s²
Include answer keys for the practice problems.
- Problem 1: 13.89 m/s
- Problem 2: 0.2 m/s
- Problem 3: 2.68 m/s²
Applications of Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration

Discuss real-world applications of speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Speed, velocity, and acceleration are important concepts in many real-world applications, including:
- Physics:Speed, velocity, and acceleration are used to describe the motion of objects in physics. For example, they are used to calculate the trajectory of a projectile or the acceleration of a car.
- Engineering:Speed, velocity, and acceleration are used in engineering to design and analyze machines and structures. For example, they are used to calculate the forces on a bridge or the speed of a rotating machine.
- Sports:Speed, velocity, and acceleration are used in sports to analyze the performance of athletes. For example, they are used to calculate the speed of a runner or the acceleration of a baseball.
Explain how these concepts are used in fields such as physics, engineering, and sports.
In physics, speed, velocity, and acceleration are used to describe the motion of objects. For example, they are used to calculate the trajectory of a projectile or the acceleration of a car.
In engineering, speed, velocity, and acceleration are used to design and analyze machines and structures. For example, they are used to calculate the forces on a bridge or the speed of a rotating machine.
In sports, speed, velocity, and acceleration are used to analyze the performance of athletes. For example, they are used to calculate the speed of a runner or the acceleration of a baseball.
Share examples of how speed, velocity, and acceleration are measured and analyzed in different contexts.
Speed, velocity, and acceleration can be measured and analyzed in different contexts using a variety of techniques. For example:
- Speedcan be measured using a speedometer or a radar gun.
- Velocitycan be measured using a GPS device or a motion sensor.
- Accelerationcan be measured using an accelerometer.
Extensions and Activities
Organize a hands-on activity or experiment that demonstrates the concepts of speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Activity:Measure the speed, velocity, and acceleration of a rolling ball.
Materials:
- A ball
- A measuring tape
- A stopwatch
Procedure:
- Roll the ball down a ramp.
- Measure the distance the ball travels.
- Measure the time it takes the ball to travel the distance.
- Calculate the ball’s speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Create a table that summarizes the key concepts and formulas related to speed, velocity, and acceleration.
| Concept | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Rate of change of position | v = d/t |
| Velocity | Rate of change of position, including direction | v = d/t |
| Acceleration | Rate of change of velocity | a = v/t |
Design a quiz or assessment to test students’ understanding of speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Quiz:
- What is the difference between speed and velocity?
- What is the SI unit of acceleration?
- A car travels 100 km in 2 hours. What is its average speed?
- A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10 m/s. What is its velocity after 1 second?
- A car accelerates from rest to a velocity of 60 mph in 10 seconds. What is its average acceleration?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures the rate at which an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that measures the rate at which an object is moving in a specific direction.
What are the units of measurement for acceleration?
The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²).
How can I calculate the acceleration of an object?
Acceleration can be calculated using the formula: acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity) / time.