Embark on a captivating journey through the realm of science 8 – electromagnetic spectrum worksheet, where we unravel the mysteries of the invisible forces that permeate our existence. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the electromagnetic spectrum, revealing its profound impact on our lives.
From the dawn of its discovery to the myriad applications that shape modern society, we will explore the fundamental properties and characteristics of electromagnetic waves, their interactions with matter, and their far-reaching implications in fields as diverse as communication, medicine, and astronomy.
Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum: Science 8 – Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
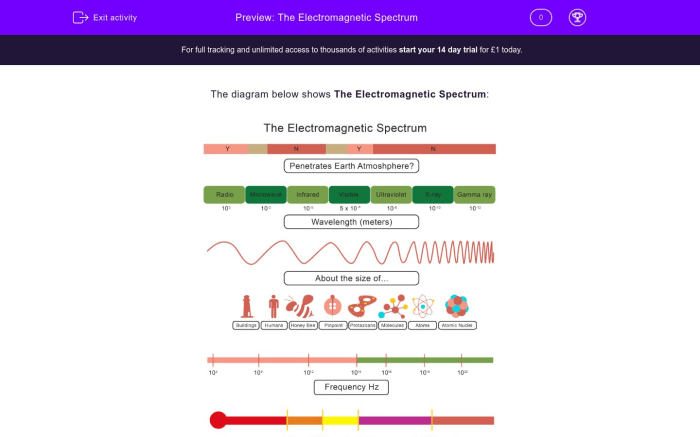
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. It encompasses all forms of electromagnetic radiation, from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays. The discovery and understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum have revolutionized our understanding of the universe and have led to numerous technological advancements.
The history of the electromagnetic spectrum can be traced back to the 19th century, when scientists began to study the properties of light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. In 1864, James Clerk Maxwell proposed the theory of electromagnetism, which unified the understanding of electricity, magnetism, and light.
Maxwell’s theory predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, which were subsequently detected by Heinrich Hertz in 1886.
Properties and Characteristics of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, and energy. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, while frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point in one second. Energy is proportional to both wavelength and frequency.
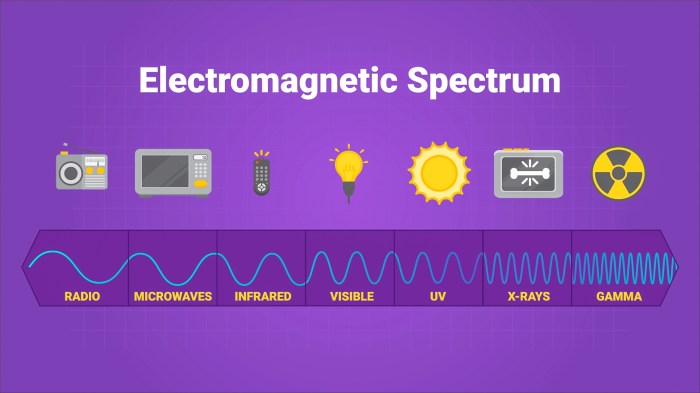
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different regions based on the properties of the waves. These regions include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. The different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are used for a wide range of applications, from communication to medicine.
Interactions of Electromagnetic Waves with Matter
Electromagnetic waves interact with matter in a variety of ways, including absorption, reflection, and transmission. Absorption occurs when electromagnetic waves are absorbed by matter, converting their energy into other forms of energy, such as heat. Reflection occurs when electromagnetic waves bounce off a surface, while transmission occurs when electromagnetic waves pass through a material.
The interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter depends on the wavelength and frequency of the waves, as well as the properties of the material. Resonance occurs when the frequency of electromagnetic waves matches the natural frequency of a material, resulting in increased absorption or transmission.
Applications of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum has a wide range of applications in different fields, including communication, medicine, and astronomy.
- Communication: Electromagnetic waves are used for communication purposes, such as radio, television, and mobile phones.
- Medicine: Electromagnetic waves are used in medical imaging, such as X-rays and MRI scans.
- Astronomy: Electromagnetic waves are used to study celestial objects, such as stars and galaxies.
The choice of which region of the electromagnetic spectrum to use for a particular application depends on the specific requirements of the application. For example, radio waves are used for long-distance communication because they can travel through obstacles, while microwaves are used for short-range communication because they can be focused into a narrow beam.
Safety Considerations and Health Effects
Exposure to different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum can have different health effects. For example, exposure to high levels of ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer, while exposure to high levels of gamma radiation can cause radiation sickness.
There are safety guidelines and regulations in place to protect people from harmful exposure to electromagnetic radiation. These guidelines and regulations vary depending on the region of the electromagnetic spectrum and the intended use of the radiation.
FAQ Compilation
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses the entire range of electromagnetic radiation, from low-frequency radio waves to high-energy gamma rays. It is a continuous spectrum, with each region characterized by its wavelength, frequency, and energy.
How do electromagnetic waves interact with matter?
Electromagnetic waves can interact with matter in various ways, including absorption, reflection, and transmission. The type of interaction depends on the wavelength of the wave and the properties of the material.
What are the applications of the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum has a wide range of applications, including communication, medicine, and astronomy. Radio waves are used for wireless communication, microwaves are used for cooking and heating, and X-rays are used for medical imaging.