The Section 14.2 Work and Machines Answer Key unveils a fascinating journey into the realm of physics, providing an in-depth understanding of the fundamental concepts that govern our world. From unraveling the intricate nature of work and energy to exploring the ingenious applications of simple and compound machines, this key unlocks a treasure trove of knowledge that empowers readers to comprehend the mechanisms that shape our daily lives.
Delving into the intricacies of simple machines, we discover the mechanical advantage they offer, enabling us to effortlessly perform tasks that would otherwise be arduous. The exploration of compound machines further reveals their remarkable ability to tackle complex operations, highlighting the synergy between individual components in achieving extraordinary outcomes.
14.2: Work and Machines: Section 14.2 Work And Machines Answer Key
Work, in the context of physics, refers to the transfer of energy from one object to another. It is quantified as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement of that object in the direction of the applied force.
Work is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction.
Examples of work being done in everyday life include lifting a book, pushing a car, and turning a screw. In each of these cases, a force is applied to an object, and the object is displaced in the direction of the force.
Work is closely related to energy. In fact, work is one way that energy can be transferred from one object to another. When work is done on an object, its energy increases. Conversely, when work is done by an object, its energy decreases.
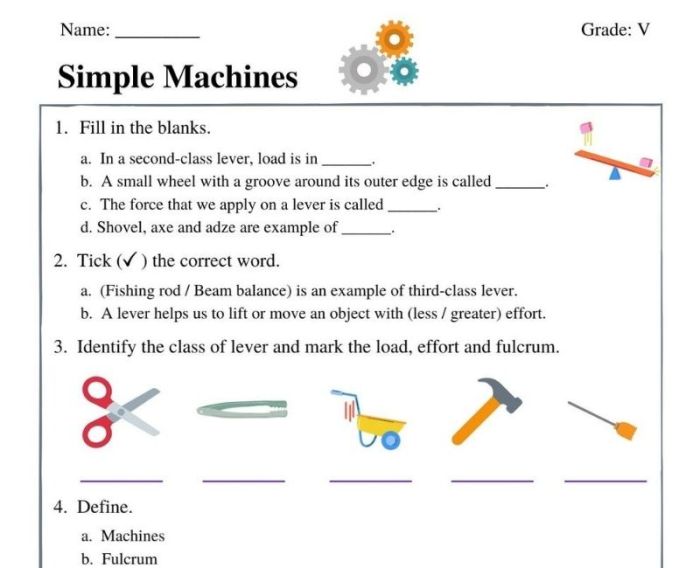
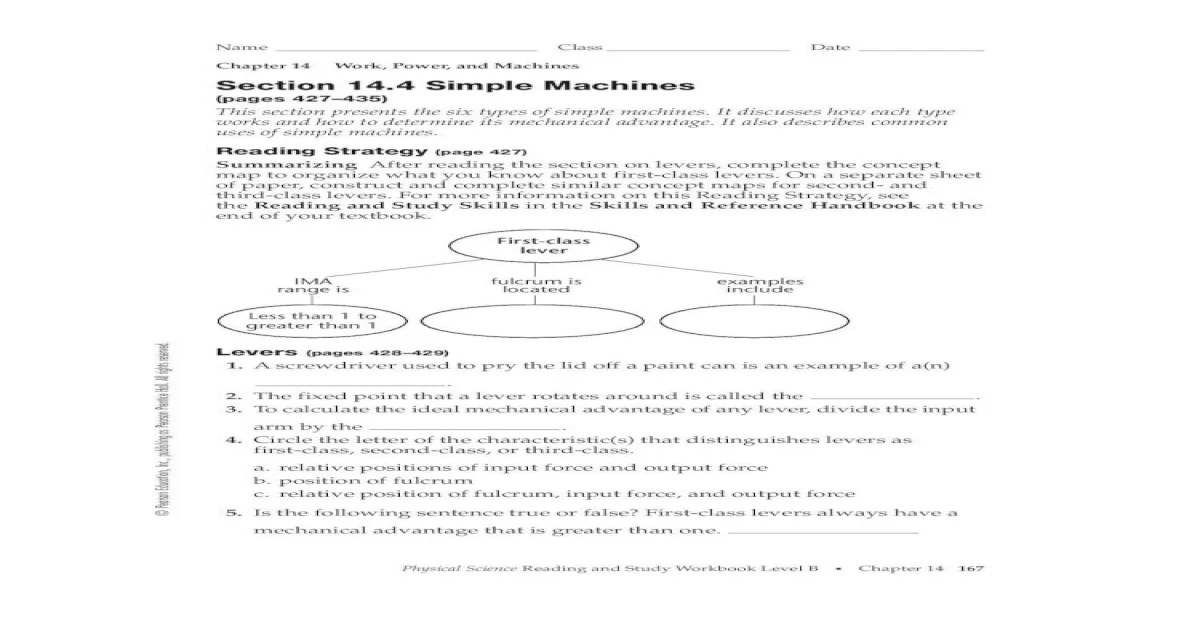
Simple Machines
Simple machines are devices that make it easier to do work. They do this by changing the direction or magnitude of the force that is applied to an object. There are six types of simple machines: the lever, the wheel and axle, the pulley, the inclined plane, the wedge, and the screw.
The mechanical advantage of a simple machine is a measure of how much easier it makes it to do work. The mechanical advantage of a machine is equal to the ratio of the output force to the input force.
Simple machines are used in a wide variety of applications, from lifting heavy objects to opening doors. They make our lives easier and more efficient.
Compound Machines, Section 14.2 work and machines answer key
Compound machines are machines that are made up of two or more simple machines. They are used to perform complex tasks that would be difficult or impossible to do with a single simple machine.
Examples of compound machines include bicycles, cars, and computers. Bicycles use a combination of levers, wheels and axles, and pulleys to make it easier to propel the bike forward. Cars use a combination of levers, wheels and axles, and gears to transmit power from the engine to the wheels.
Compound machines are more efficient than simple machines because they can multiply the force that is applied to an object. This makes it possible to do more work with less effort.
Efficiency of Machines
The efficiency of a machine is a measure of how much of the input energy is converted into output energy. The efficiency of a machine is always less than 100% because some of the input energy is always lost to friction and other inefficiencies.
There are a number of factors that affect the efficiency of a machine, including the type of machine, the materials used to make the machine, and the condition of the machine.
There are a number of ways to improve the efficiency of a machine, including using better materials, reducing friction, and using more efficient designs.
Power
Power is a measure of the rate at which work is done. The power of a machine is equal to the amount of work that the machine does per unit time.
There are a number of factors that affect the power of a machine, including the force that the machine applies, the speed at which the machine does work, and the efficiency of the machine.
There are a number of ways to increase the power of a machine, including increasing the force that the machine applies, increasing the speed at which the machine does work, and improving the efficiency of the machine.
Applications of Machines
Machines are used in a wide variety of applications, from manufacturing to transportation to medicine. They make our lives easier, more efficient, and more productive.
Machines have revolutionized the way we live and work. They have made it possible to do things that would have been impossible without them.
The ethical implications of using machines are complex. On the one hand, machines can be used to improve our lives and make the world a better place. On the other hand, machines can also be used for harmful purposes, such as war and oppression.
General Inquiries
What is the definition of work in physics?
Work is the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied to an object, resulting in the displacement of that object.
How are simple machines used to make work easier?
Simple machines provide a mechanical advantage, reducing the amount of force required to perform a task by altering the direction or magnitude of the applied force.
What is the difference between efficiency and power?
Efficiency measures the ratio of useful output energy to the total input energy, while power quantifies the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.