Crisis plans should be RBT is a comprehensive guide for behavioral health professionals on developing and implementing effective crisis plans. It provides a clear and concise overview of the essential components of a crisis plan, the role of Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) in crisis management, and the ethical considerations for RBTs when working with individuals in crisis.
This guide is essential reading for any RBT working with individuals in crisis. It provides the knowledge and skills necessary to develop and implement effective crisis plans that can help to prevent and manage crisis situations.
Crisis Plans and RBT

Crisis plans are essential tools in behavioral health settings. They provide a roadmap for responding to individuals experiencing a mental health crisis, ensuring their safety and well-being. Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) play a crucial role in crisis plan development and implementation, utilizing their specialized knowledge and skills to support individuals in distress.
Crisis plans should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure their effectiveness. This is especially important for organizations like nc state lambda chi alpha , which face unique challenges and risks. By keeping crisis plans up-to-date, organizations can be better prepared to respond to and manage crises, minimizing their impact and ensuring the safety and well-being of their members and stakeholders.
Ethical Considerations for RBTs
RBTs must adhere to strict ethical guidelines when working with individuals in crisis. These include maintaining confidentiality, respecting client autonomy, and avoiding any actions that could harm or exploit the individual. RBTs must also be aware of their own limitations and seek supervision or support when necessary.
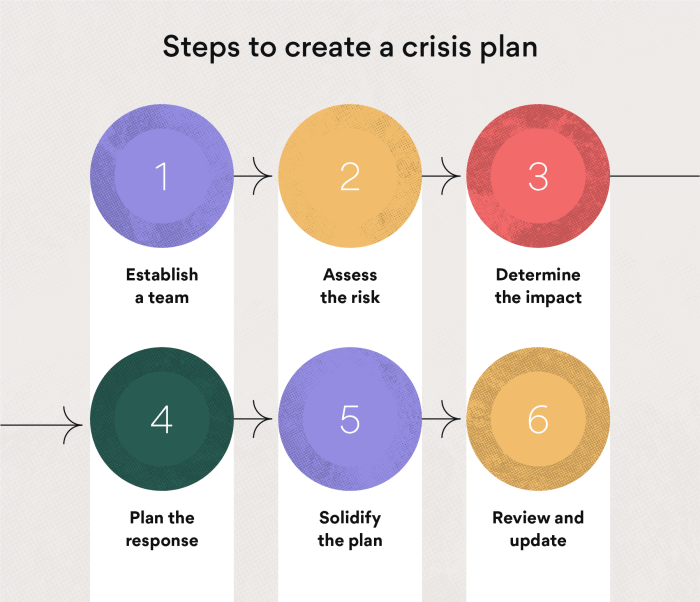
Components of Effective Crisis Plans

Effective crisis plans provide a roadmap for organizations to navigate challenging situations and minimize their impact. They encompass essential elements that guide response, communication, and recovery efforts.
Crisis plans should be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each organization. A comprehensive plan includes the following components:
Crisis Management Team
- Identifies the individuals responsible for crisis management and their roles.
- Artikels the decision-making process and communication protocols within the team.
Risk Assessment
- Identifies potential crisis scenarios and their likelihood of occurrence.
- Assesses the potential impact of each crisis scenario on the organization.
Response Protocols, Crisis plans should be rbt
- Artikels the specific actions to be taken in the event of a crisis.
- Includes protocols for communication, evacuation, and other emergency procedures.
Communication Plan
- Establishes the channels and methods for communicating with stakeholders during a crisis.
- Identifies the key messages to be conveyed and the designated spokesperson.
Recovery Plan
- Artikels the steps for restoring normal operations after a crisis.
- Includes procedures for assessing damage, providing support to affected individuals, and evaluating the effectiveness of the crisis response.
RBTs’ Responsibilities in Crisis Management: Crisis Plans Should Be Rbt
RBTs play a vital role in crisis management by providing assessment, intervention, and coordination services. Their responsibilities include:
Assessing and Responding to Crisis Situations
RBTs are trained to assess and respond to crisis situations using evidence-based techniques. They can identify potential triggers, assess the individual’s risk of harm, and develop appropriate interventions. RBTs use de-escalation strategies to calm and manage individuals in crisis, ensuring their safety and well-being.
Techniques and Strategies for De-escalation and Management
RBTs employ various techniques to de-escalate and manage individuals in crisis, including:
- Active listening: RBTs listen attentively to the individual’s concerns, validating their feelings and experiences.
- Empathy: RBTs demonstrate empathy and understanding, building rapport and trust with the individual.
- Problem-solving: RBTs work with the individual to identify and address underlying issues contributing to the crisis.
- Crisis intervention techniques: RBTs use specific techniques, such as grounding exercises, to help the individual regulate their emotions and cope with the crisis.
Coordinating with Other Professionals and Agencies
RBTs often collaborate with other professionals and agencies during crisis interventions. They provide information about the individual’s condition and needs, coordinate services, and ensure a seamless transition between different care settings. RBTs also advocate for the individual’s rights and ensure their well-being throughout the crisis management process.
Training and Support for RBTs in Crisis Planning

Training and support are crucial for Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) working with individuals in crisis situations. This involves identifying their specific training needs, developing comprehensive training programs, and providing ongoing supervision and support.
RBTs working in crisis settings may encounter various challenges, including managing aggressive behaviors, providing emotional support, and collaborating with other professionals. To effectively handle these challenges, they require specialized training that equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Identifying Training Needs
- Assess the specific risks and challenges faced by RBTs working with individuals in crisis.
- Conduct surveys or interviews with RBTs to identify their training gaps and areas where they need additional support.
- Review relevant literature and best practices in crisis management to identify essential competencies for RBTs.
Developing Training Programs
- Develop comprehensive training programs that cover essential topics such as crisis assessment, intervention strategies, safety protocols, and self-care.
- Incorporate hands-on practice, role-playing, and simulations to enhance RBTs’ skills and confidence.
- Ensure training programs are evidence-based and aligned with best practices in crisis management.
Ongoing Supervision and Support
Ongoing supervision and support are essential for RBTs working in crisis settings. This involves:
- Regular supervision sessions to provide guidance, feedback, and support.
- Access to consultation and support from experienced professionals, such as psychologists or social workers.
- Creating a supportive work environment that promotes open communication and collaboration.
By providing comprehensive training and ongoing support, organizations can empower RBTs to effectively manage crisis situations and ensure the safety and well-being of individuals in their care.
FAQ Overview
What is a crisis plan?
A crisis plan is a written document that Artikels the steps that an individual will take in the event of a crisis. It includes information on how to identify a crisis, who to contact for help, and what to do to manage the crisis.
What is the role of an RBT in crisis planning?
RBTs play a vital role in the development and implementation of crisis plans. They have the knowledge and skills to assess and respond to crisis situations and can help to de-escalate and manage individuals in crisis.
What are the ethical considerations for RBTs when working with individuals in crisis?
RBTs must always act in the best interests of their clients. They must respect the client’s confidentiality, autonomy, and dignity. They must also be aware of their own limitations and seek supervision when necessary.